Introduction
The aim of this tutorial is to deploy Django applications on Internet Information Services (IIS). We'll cover two deployment methods with detailed configuration steps and visual guides.
Note
This tutorial assumes basic knowledge of Django and Python. We'll guide you through the IIS-specific configurations.
Two Deployment Methods:
HttpPlatform Handler
Microsoft's recommended approach for modern Python web applications.
FastCGI Handler (WFastCGI)
Legacy method, no longer actively maintained but still functional.
Prerequisites
Environment
- Windows Server 2019 (or compatible)
- IIS with Management Tools
- Python 3.11+ installed
- Django 4.1.7+ installed
Required Downloads
1 Install Python & Django
Install Django using pip
pip install Django==4.1.7Verify Installation
Check Python Version:
python --versionCheck Django Version:
py -m django --versionExpected Output:
C:\Users\azureuser>python --version
Python 3.11.2
C:\Users\azureuser>py -m django --version
4.1.72 Create Django Application
We'll create a basic Django application following the official Django tutorial. This will be created under C:\sites\site01
Django Project Structure
Understanding the basic Django project structure:
- mysite/ - Root directory container for your project
- manage.py - Command-line utility for Django project interaction
- mysite/settings.py - Settings/configuration for Django project
- mysite/urls.py - URL declarations (table of contents)
- mysite/wsgi.py - Entry-point for WSGI-compatible web servers
- mysite/asgi.py - Entry-point for ASGI-compatible web servers
Project Directory Structure
C:\sites\site01>tree /F
C:.
└───mysite
│ db.sqlite3
│ manage.py
│
├───logs
├───mysite
│ │ asgi.py
│ │ settings.py
│ │ urls.py
│ │ wsgi.py
│ │ __init__.py
│ │
│ └───__pycache__
│ settings.cpython-311.pyc
│ urls.cpython-311.pyc
│ wsgi.cpython-311.pyc
│ __init__.cpython-311.pyc
│
└───polls
│ admin.py
│ apps.py
│ models.py
│ tests.py
│ urls.py
│ views.py
│ __init__.py
│
├───migrations
│ __init__.py
│
└───__pycache__
urls.cpython-311.pyc
views.cpython-311.pyc
__init__.cpython-311.pycTest Django Application
py manage.py runserverThis will run the development server at http://localhost:8000

Django Polls Application Interface
Important Note:
Create a logs folder in your project directory. This will be used later for IIS logging configuration.
3 IIS Installation & Configuration
Install IIS
Both deployment methods require IIS. You can install it through Server Manager or PowerShell:
Install-WindowsFeature -name Web-Server -IncludeManagementToolsConfigure Feature Delegation
Both methods require editing Handler Mappings, which by default has read-only permissions. We need Read/Write access:
Path: IIS Manager → Server Level → Feature Delegation → Handler Mappings → Read/Write
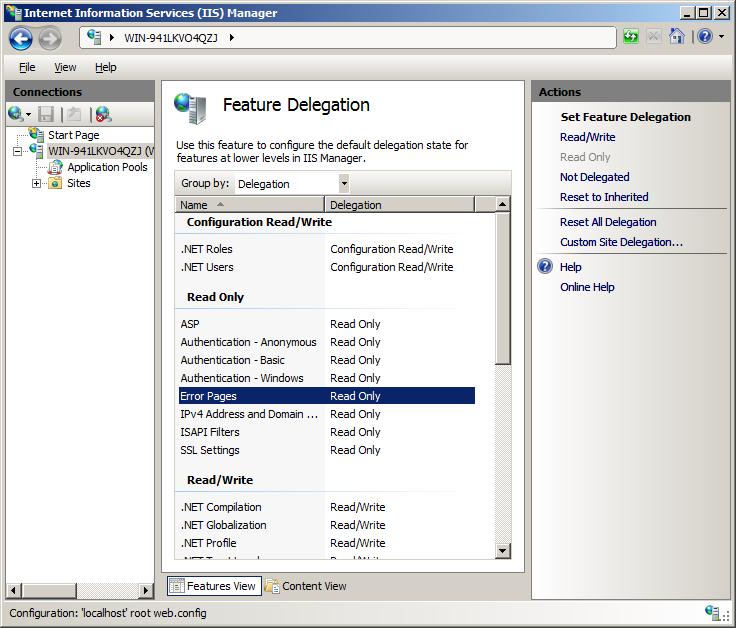
IIS Feature Delegation Settings
Create Two Sites
We'll create two separate sites to demonstrate both deployment methods:
Site01 - HttpPlatform
- Port: 8001
- Path: C:\sites\site01
- Method: HttpPlatform Handler
Site02 - WFastCGI
- Port: 8002
- Path: C:\sites\site02
- Method: WFastCGI Handler
Method 1: HttpPlatform Handler (Recommended)
Why HttpPlatform Handler?
Microsoft recommends HttpPlatform handler as it's actively maintained and provides better process management for Python applications.
Step 1: Download HttpPlatform Handler
Download and install the HttpPlatformHandler v1.2 from Microsoft:
Download HttpPlatformHandlerWhat it does:
- Process management of HTTP Listeners
- Proxy requests to the managed process
- Works with any process that can listen on a port (Python, Node.js, etc.)
Step 2: Configure httpPlatform Settings
Navigate to: IIS Manager → Sites → Site01 → Configuration Editor → system.webServer/httpPlatform
| Setting | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| processPath | C:\Python311\python.exe |
Path to Python executable |
| arguments | C:\sites\site01\mysite\manage.py runserver %HTTP_PLATFORM_PORT% |
Django management command with dynamic port |
| stdoutLogEnabled | true |
Enable logging output |
| stdoutLogFile | C:\sites\site01\mysite\logs |
Path for log files |
Step 3: Configure Environment Variables
Navigate to: IIS Manager → Sites → Site01 → Configuration Editor → appSettings
Required Environment Variables:
PYTHONPATH = C:\sites\site01\mysite
WSGI_HANDLER = django.core.wsgi.get_wsgi_application()
DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE = mysite.settingsStep 4: Add Handler Mapping
Navigate to: IIS Manager → Sites → Site01 → Handler Mappings → Add Module Mapping
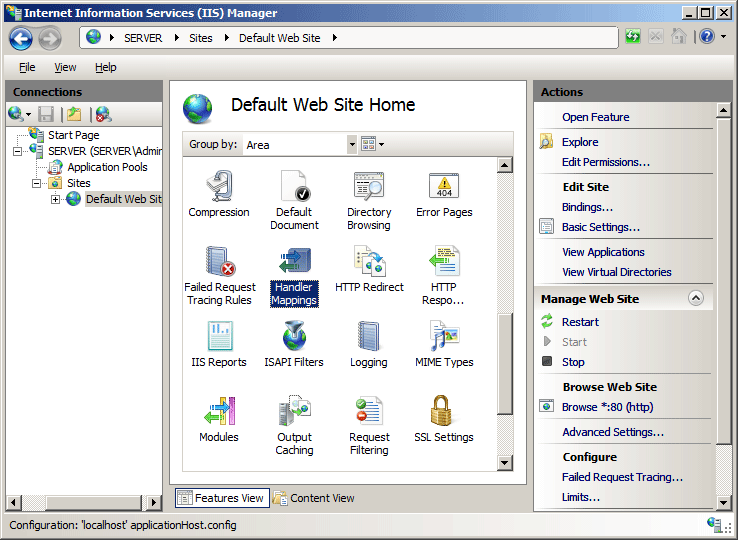
IIS Handler Mappings Configuration
Handler Mapping Settings:
- Request path: *
- Module: httpPlatformHandler
- Name: MyPyHandler (or any name)
Important: Click "Request Restrictions" and uncheck "Invoke handler only if request is mapped to"
Step 5: Complete web.config
Your final web.config should look like this:
Test Your Configuration
Navigate to http://localhost:8001/polls to test your Django application running on IIS with HttpPlatform handler.
Method 2: WFastCGI Handler (Legacy)
Legacy Method
WFastCGI is no longer actively maintained by Microsoft, but still functional for existing deployments.
Step 1: Install WFastCGI
pip install wfastcgiStep 2: Install CGI Module for IIS
Install-WindowsFeature -name Web-CGIClose and reopen IIS Manager to see the new FastCGI module.
Step 3: Configure FastCGI Application
Navigate to: IIS Manager → Server Level → FastCGI → Add Application
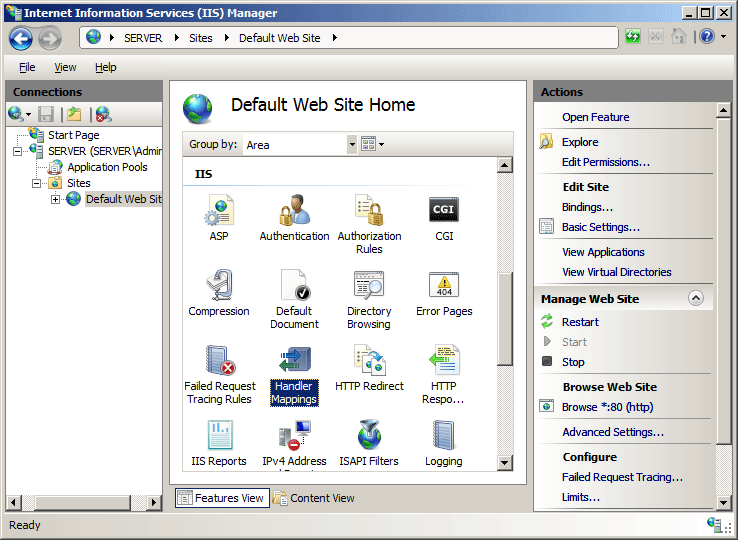
FastCGI Application Configuration
FastCGI Settings:
- Full Path: C:\Python311\python.exe
- Arguments: C:\Python311\Lib\site-packages\wfastcgi.py
Step 4: Add Handler Mapping
Navigate to: IIS Manager → Sites → Site02 → Handler Mappings → Add Module Mapping
Handler Mapping Settings:
- Request Path: *
- Module: FastCgiModule
- Executable: C:\Python311\python.exe|C:\Python311\Lib\site-packages\wfastcgi.py
- Name: MyPyHandler2 (or any name)
Important: Uncheck "Invoke handler only if request is mapped to" in Request Restrictions.
Step 5: Configure App Settings
Navigate to: IIS Manager → Sites → Site02 → Configuration Editor → appSettings
PYTHONPATH = C:\sites\site02\mysite
WSGI_HANDLER = django.core.wsgi.get_wsgi_application()
DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE = mysite.settingsStep 6: Complete web.config
Step 7: FastCGI Configuration File
The FastCGI section is stored in C:\Windows\System32\inetsrv\Config\applicationHost.config:
Test Your Configuration
Navigate to http://localhost:8002/polls to test your Django application running on IIS with WFastCGI handler.
Troubleshooting & Tips
Common Issues
- • 500 Internal Server Error - Check logs folder
- • Handler not found - Verify module installation
- • Python path errors - Check PYTHONPATH setting
- • Port conflicts - Ensure ports 8001/8002 are free
- • Permission issues - Check IIS app pool identity
Best Practices
- • Use HttpPlatform for new deployments
- • Always enable logging for debugging
- • Create separate app pools for each site
- • Monitor performance and resource usage
- • Keep Python and Django updated
Log File Locations
# HttpPlatform logs
C:\sites\site01\mysite\logs\
# IIS logs
C:\inetpub\logs\LogFiles\
# Windows Event Logs
Event Viewer → Windows Logs → ApplicationPerformance Optimization
- FastCGI: Adjust maxInstances and recycling settings
- HttpPlatform: Consider using production WSGI servers like Gunicorn
- Static Files: Configure IIS to serve static files directly
- Caching: Implement appropriate caching strategies
Method Comparison
| Feature | HttpPlatform Handler | WFastCGI |
|---|---|---|
| Maintenance Status | ✓ Actively maintained | ✗ No longer maintained |
| Microsoft Recommendation | ✓ Recommended | ~ Legacy support |
| Setup Complexity | ✓ Simpler configuration | ~ More complex setup |
| Process Management | ✓ Better process handling | ~ Basic process management |
| Performance | ✓ Good for development/testing | ✓ Can be optimized for production |
Conclusion
You now have two working methods to deploy Django applications on IIS. Both approaches have their merits:
Choose HttpPlatform Handler if:
- • Starting a new deployment
- • Want Microsoft's recommended approach
- • Need simpler configuration
- • Prefer active maintenance and support
Choose WFastCGI if:
- • Working with existing deployments
- • Need specific FastCGI features
- • Have experience with CGI configuration
- • Comfortable with legacy systems
Recommendation: For production deployments, consider using dedicated WSGI servers like Gunicorn or uWSGI behind IIS as a reverse proxy for better performance and scalability.